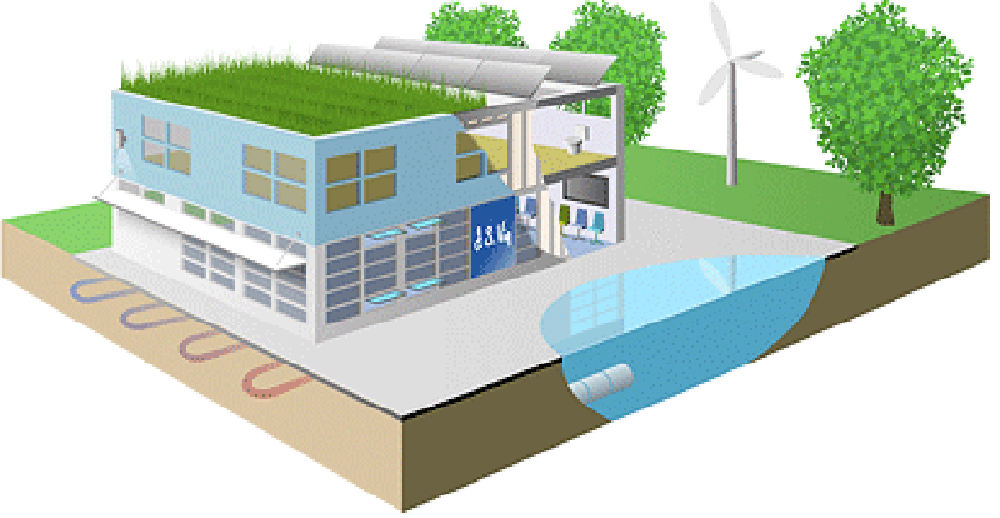
Best Practices
The J.S. Vig Project Green team audits a new construction project or existing building operation through benchmarking and careful evaluation. At the audit’s conclusion, we propose best practices derived from industry standards (LEED, Energy Star®, ISO 14000) and emerging technologies.
We then simplify the expanding universe of sustainable construction and adapt it to the best 5-20 building practices that meet a project’s specific needs, using a cost/benefit approach.
J.S. Vig offers these best practices to the client in a menu format – where they can select individual strategies based upon the cost/benefit analysis we provide.
After the sustainable practices are implemented, the Project Green team will continue to ensure that all systems are operated and maintained optimally through measurement and verification practices.
Green construction best practices include: